Relieve Pain, Restore Balance, Move Freely
- Call Today +91-9790799944
- Open Hour 09:00 AM to 21:00 PM
Shin splints, medically known as medial tibial stress syndrome, cause pain along the front or inside edge of the shinbone. This condition is often associated with overuse or repetitive stress from activities like running, jumping, or walking on hard surfaces. Poor biomechanics, such as overpronation, flat feet, or inadequate footwear, can exacerbate the problem. Shin splints often develop gradually, presenting as discomfort or tenderness in the lower leg, which may worsen with activity. Early intervention through rest, proper stretching, and osteopathic care can alleviate symptoms and prevent chronic issues. Addressing underlying factors, such as gait imbalances or muscle weaknesses, ensures long-term recovery and reduces the likelihood of recurrence.
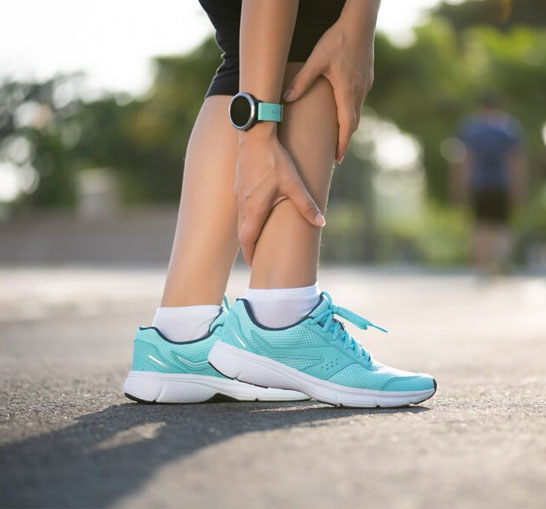

Relieve Pain, Restore Balance, Move Freely
Repeated strain, improper biomechanics, and inadequate footwear contribute to shin splints, causing persistent discomfort.
Repetitive stress on shin muscles and bones causes inflammation, leading to persistent pain and discomfort.
Incorrect foot alignment or gait abnormalities increase strain on shins, contributing to frequent injuries.
Wearing unsupportive shoes fails to absorb shock, intensifying pressure and stress on the lower legs.
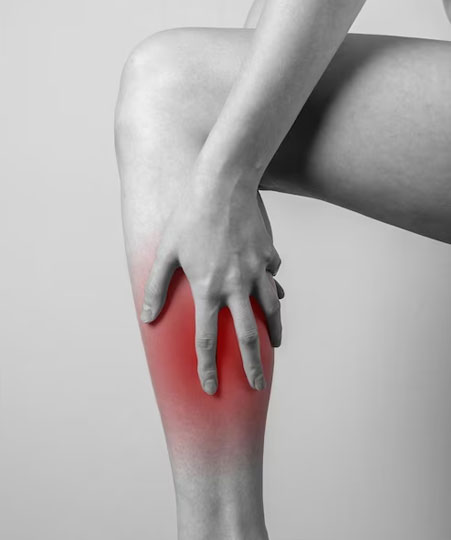
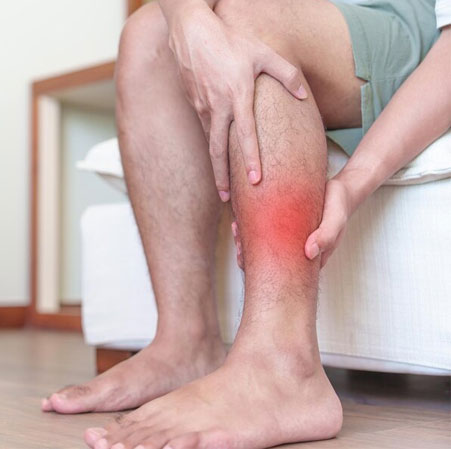
Avoiding shin splints involves a combination of proper training, footwear, and self-care. Start by gradually increasing exercise intensity to prevent overloading your lower legs. Invest in supportive shoes tailored to your activity and foot structure, ensuring optimal arch and heel support. Incorporate stretching and strengthening routines to enhance flexibility and stability in your calves and shins. Pay attention to running surfaces, opting for softer terrains to reduce impact stress. Address biomechanical issues, such as overpronation, with orthotics or expert guidance. Regular rest and recovery play a vital role in minimizing strain and inflammation. These preventive measures collectively promote lasting lower leg health and reduce recurrence risks.
Rest is essential to allow your shins to recover. Adequate recovery time helps reduce inflammation, easing discomfort.
Physical therapy focuses on strengthening muscles around the shin, improving flexibility, and correcting movement patterns.
Wearing proper footwear with adequate arch support and using orthotics can reduce pressure on the shins.
Stretching and strengthening exercises are essential for alleviating and preventing shin splints. Targeted stretches like calf and Achilles tendon stretches reduce tension and improve flexibility in key muscles. Strengthening exercises, such as toe raises and ankle resistance workouts, build stability and support the lower leg. These exercises enhance muscle endurance and balance, minimizing strain during activities. Incorporating dynamic stretches before physical activity and static stretches afterward promotes recovery and reduces future injury risks. By improving alignment and reinforcing proper movement patterns, these exercises address the root causes of shin splints. A consistent routine can lead to significant improvement in pain relief and overall performance.
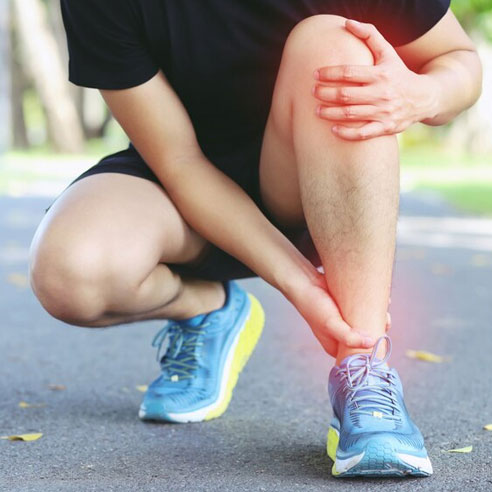

Discover relief with personalized treatments and holistic therapies designed to heal shin splints and restore mobility.
Targeted techniques address underlying causes, improving biomechanics and reducing shin splint pain effectively.
Tailored recovery programs focus on restoring muscle balance, enhancing flexibility, and preventing future injuries.
Osteopathic manipulation eases tension, improves circulation, and promotes natural healing for lasting shin splint relief.
Correcting posture and alignment supports overall musculoskeletal health, reducing strain and aiding swift recovery.
Shin splints often arise from overuse, improper footwear, or poor running techniques, leading to muscle strain.
Rest, ice, stretching, and proper footwear can help alleviate shin splint discomfort effectively.
Ignoring shin splints can lead to stress fractures or chronic pain requiring longer recovery.
Yes, osteopathy improves alignment, mobility, and muscle function to address underlying shin splint issues.
© All Rights Reserved by Kriston Healthcare